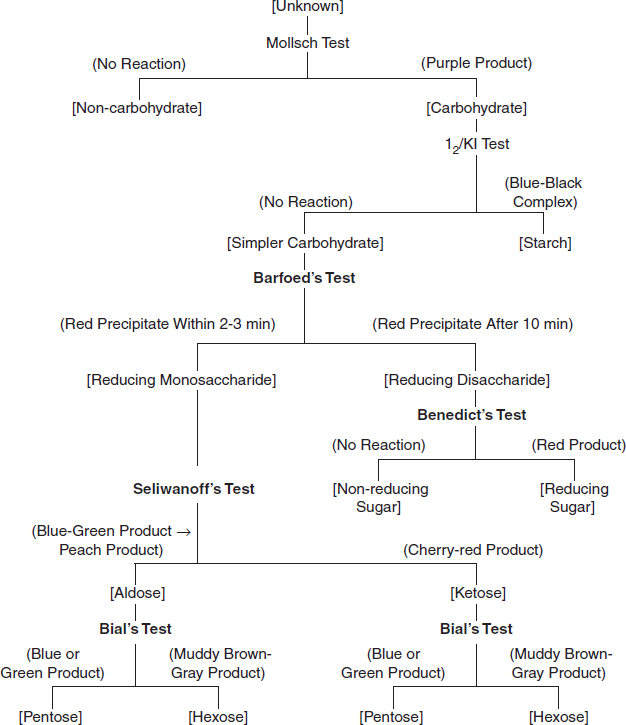
Tests for Carbohydrates- Principle, Procedures, Result, Interpretation
The note on tests for carbohydrates provides an overview of qualitative and quantitative tests used to analyze carbohydrates.
Tests for Carbohydrates- Principle, Procedures, Result, Interpretation Read More »