Introduction:
The unavoidable by-product of human activities results in a solid waste which tends to increase with rapid urbanization, improved living standards and changing consumption patterns. It is the unwanted or useless solid materials generated from combined residential, industrial and commercial activities in a given area. Solid waste management a critical component that include collection, transportation, and disposal of waste materials. Moreover, it is the process of removal of different types of solid waste in specific manner that it does not cause any problem to environment and also the living organism. It is performed and executed through diverse methods which totally depends upon the category of the solid waste and site of the waste.
Depending on their physical state wastes are classified as liquid wastes, gaseous wastes and solid wastes.
Classification:
Based on their sources of origin
Residential wastes, Commercial wastes, Institutional waste, Municipal wastes, Industrial wastes, Agricultural wastes, Institutional waste
Based on physical nature
Garbage: Residual vegetable or animal wastes resulting from the handling, preparation, cooking and eating of foods that are putrescible, and easily decomposable.
Ashes: Burning wood, coal, coke, and other combustible wastes produces residues.
Combustible and non-combustible wastes: Combustible solid wastes, as paper, cardboard, plastics, textile, rubber, leather, wood, furniture and garden trimmings. Non-combustible solid wastes as glass, crockery, tin cans, ferrous and nonferrous metals.
Demolition and construction wastes: Inert wastes include stones, soil, concrete, bricks, plumbing, heating, and other electrical parts.
Hazardous wastes
Methods for the treatment of the solid waste:
Open Dumps
It refer to uncovered areas that are used to dump solid waste of all kinds where the waste is neither treated nor segregated. Such open dumps are major responsible of spreading disease because it is breeding sites for flies, rats, and other insects.
Landfills
It refer to the ground or site for disposal of waste materials that has been filled in with rocks and soil, so that it can be used for a specific purpose, such as for building houses.
Older, poorly designed or poorly managed landfills can lead a number of adverse environmental impacts such as wind-blown litter, attraction of vermin, and generation of liquid leachate.
Biological Digestion
This treatment methods, such as aerobic and anaerobic digestion, use microorganisms to break down organic waste. These processes can produce biogas for energy generation and nutrient-rich byproducts for soil amendment.
Composting
It is the biological decomposition of organic waste (paper, agricultural and food wastes) under controlled aerobic or anaerobic condition in order to yield good manure such as solid, carbon dioxide, water vapor and energy.
Different stages of composting
- Segregation of solid waste
- Processing the compostable matter
- Preparation for compost
- Digestion
- Curing
Mechanism:
Composting is a very complex process which involves the participation of several microorganisms like bacteria, actinomycetes and fungi that bring out the decomposition of macromolecule namely cellulose, proteins, lipids, and other complex organic compounds.With the reference to changes in temperature composting can be classified into :
- Mesophilic stage
- Thermophilic stage
- Cooling stage
Four main groups of bacteria involved in anaerobic digestion,
Hydrolytic fermentative bacteria – Clostridium and Peptococcus
Acetogenic bacteria – Syntrophobacter and Syntrophomonas.
Acidogenic bacteria – Methanosarcina and Methanothrix.
Methanogenic bacteria – Methanobacterium and Methanobrevibacterium
Vermicomposting
It is a simple biotechnological and natural process of composting, in which certain species of earthworms are used to convert the waste material with rigid structures into compost. Eventually, the compost is used as a natural fertilizer for enhancing plant growth which is one to most used high-quality manure in modern era.
Encapsulation
Solid particulate waste material is coated with a non-reactive and thermosetting resin such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polybutadiene to perform encapsulation. The managing of waste from the nuclear industry is very challenging because it can pollute the environment and transfer toxins to soil-plant-animal food chains.
Since decades, in order to manage the hazardous effect radioactive wastes encapsulation by the cement has been used because it is inexpensive, can be easily prepared and handled. Likewise, the environmental impact of radioactive waste is also limited by the use of natural zeolite as encapsulation.
Encapsulation method are of the types:
- Microencapsulation
- Microencapsulation
Incineration
Incineration is the most common thermal treatment process. It is burning of the waste at a temperature of 1000°C ± 100°C in the presence of oxygen so as to eliminate all odors and to ensure good combustion. After incineration, the hazardous wastes are converted into less hazardous components such as carbon dioxide, water vapor and ash.
Management of Solid waste:
The fundamental objective of waste processing is to reduce the number of wastes through recycling and disposal of waste in a way not to impair environmental conservation.
Refuse, reuse, recycle, reduce are the main moto of the management of solid wastes.
The management of the solid waste is executed on the according to the nature of the wastes:
- Management of Medical solid waste
- Management of non-degradable solid waste
- Management of Hazardous waste
- Management of non-hazardous & biodegradable solid waste
- Management of electronic waste “e-waste”
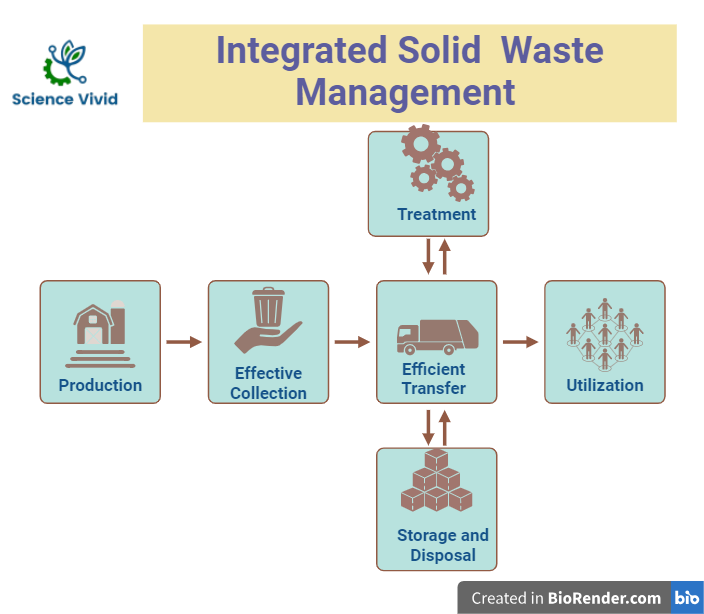
Fig: Integrated Solid waste management
Factors affecting solid waste management:
- Economic status, knowledge, attitude and status of the population
- Geography, location, and Topography
- Nature and types of wastes
- Climate, weather, temperature, and season
- Resources, human resources and infrastructure available
