Cystic Fibrosis- Definition, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
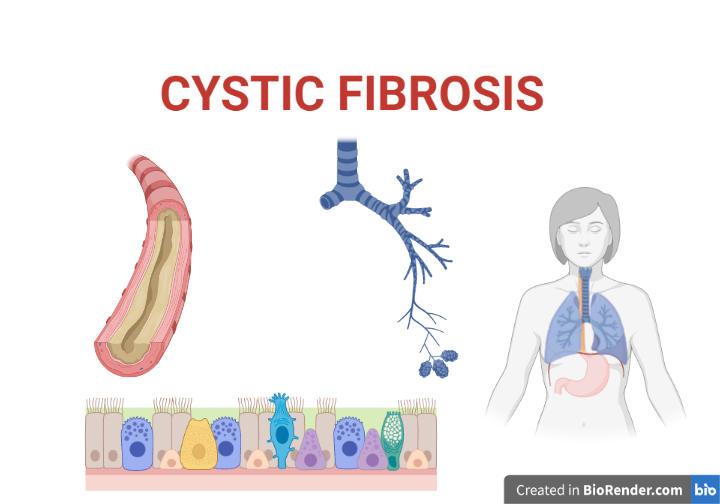
Introduction: Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a hereditary condition that impacts the respiratory, digestive, and reproductive systems. It is caused by a mutation in the gene that codes for a protein called cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). This protein regulates the movement of salt and water in and out of cells, and is involved in […]
Cystic Fibrosis- Definition, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment Read More »