Introduction:
- Since its beginnings in 1869, Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) extraction has progressed significantly.
Many of the potential downstream applications in the field of molecular biology require it as the first step. (PCR, DNA cloning, DNA sequencing, DNA electrophoresis) Next-generation sequencing, PCR, DNA cloning, DNA sequencing, DNA electrophoresis) - DNA extraction is a technique for isolating DNA from cell membranes, proteins, and other biological components from a sample using physical and/or chemical processes. Several parameters, such as tissue type and DNA integrity, must be considered when selecting a DNA extraction method.
- Phenol-chloroform isoamyl alcohol, Proteinase K, CTAB method, spin column-based approaches, and magnetic bead-based technology are some of the different types of DNA extraction methods available. The procedure to utilize, on the other hand, is determined by the sample type and the purity and quantity of DNA we wish to obtain.
- Every DNA extraction process differs depending on the type of sample; for instance, plant DNA extraction differs from blood DNA extraction. Similarly, the process for isolating bacterial DNA differs from those used for other kinds. As a result, different DNA isolation procedures are required for various samples.
History:
In 1869, Friedrich Miescher made the first attempt at DNA extraction. He extracted the cell substance and termed it “nuclei,” which was later named “nucleic acid” by his trainee. He invented a method for nucleic acid isolation by accident, but he wasn’t sure if the nucleic acid he extracted was DNA.
Meselson and Stahl later established a full-function DNA extraction procedure in 1958. The first methodology for recovering DNA from E. coli bacteria was the density gradient centrifugation protocol.
Lahiri and Nurnberger introduced the proteinase K enzyme technique of DNA extraction protocol in 1991. They even used the Nonidet P40 and SDS to modify the technique. Miller et al., however, reported on the use of proteinase K in DNA extraction in 1988.
Joseph Sambrook and David W. Russell pioneered the phenol-chloroform isoamyl alcohol technique, which has become increasingly popular in recent years. Among researchers, the current method is the most popular.
What is DNA extraction?
“Extracting DNA from cells” is the most basic definition of DNA extraction. Depending on the method, chemical, and test employed, we can explain it in a variety of ways. Here are a few different definitions of DNA extraction:
“A DNA extraction is the process of isolating DNA by breaking the cell wall/cell membrane and the nuclear membrane.”
“A DNA extraction is described as the separation of DNA from the cell membrane and nuclear membrane using chemicals, enzymes, or physical disturbances.”
“Nucleic acid extraction” or “DNA extraction” is the process of extracting nucleic acid from the rest of the cell organelle.
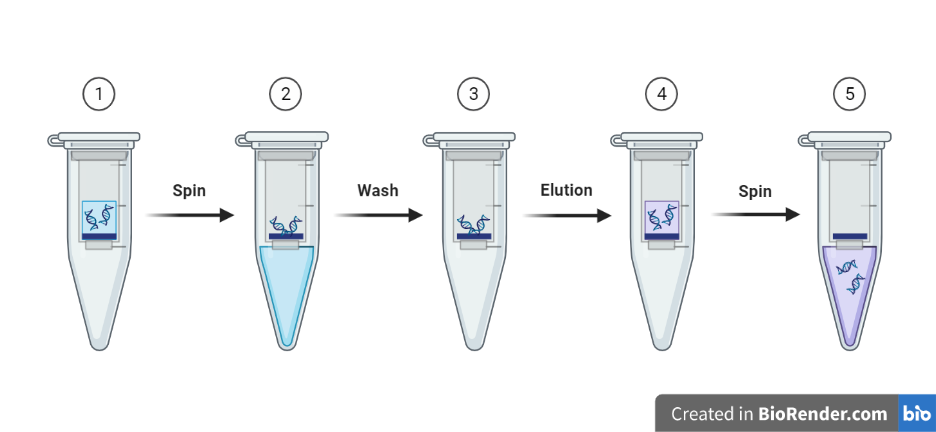
Fig: Outline of DNA extraction
How to obtain DNA?
The cytoplasm and cell membrane/cell wall make up the cell. Several organelles, such as mitochondria, ribosomes, nucleus, and endoplasmic reticulum, are found in the cytoplasm. The cell wall is absent in animal cells, although it is present in plant cells and (most) bacterial cells.
To isolate DNA-deoxyribonucleic acid, we must first breach the cell wall/cell membrane, as well as the nuclear envelope. Other cellular organelle debris must also be removed. Precipitation and purification of the DNA are the final steps.
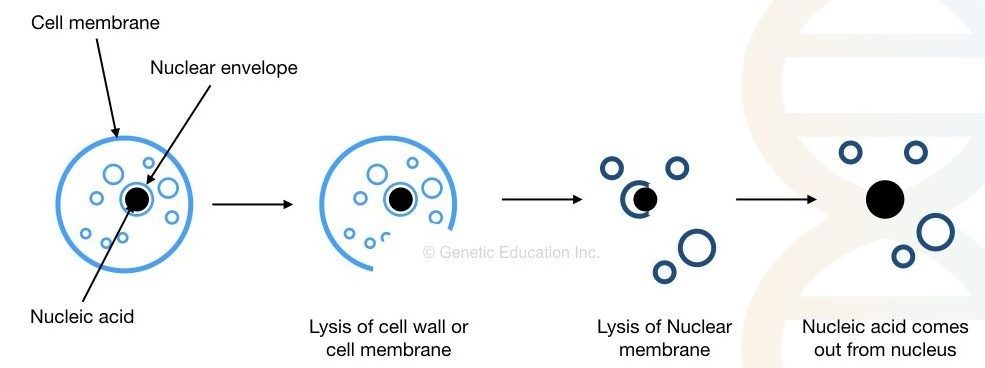
Fig: Extraction of DNA
In other words, cell lysis, precipitation, and dissolving DNA are the three major processes in the DNA isolation process. The following are the outline of the process.
Lysis of cell wall/ cell membrane
- Chemical disruption
- enzymatic disruption
- Mechanical disruption
Lysis of nuclear membrane:
- Chemical lysis
- Enzymatic lysis
Removing cell debris
- Centrifugation
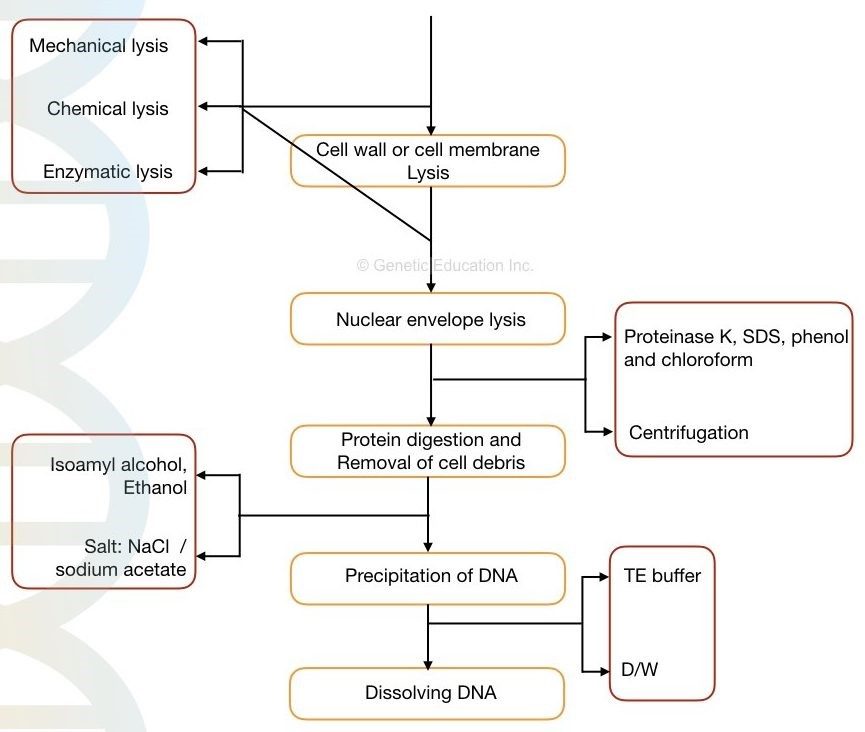
Fig: Different principle of DNA extraction
For various objectives, different compounds and combinations of chemicals are used. Protein and lipids almost entirely make up the nuclear and cell membranes. As a result, the same compounds can be used for both.
By solubilizing the cell wall/cell membrane, chemicals like SDS, CTAB, Tris, and other detergents can lyse them. Every chemical serves a certain purpose.
Proteinase K, peptidase, and protease are enzymes that break down proteins. Because it directly targets amino acid linkages and digests the protein, the enzyme functions better than any other chemical.
Furthermore, the procedure for extracting DNA varies based on the cell type.
Cells with a soft cell wall:
Some bacteria have a cell wall that is exceedingly smooth and fragile. M. tuberculosis, for example, has a smooth cell wall. We can lyse the cell wall by gently heating the bacterial solution.
The supernatant can be used directly for PCR. We can also achieve a good quality PCR result by directly placing the bacterial culture into the PCR tube for 15 minutes at first denaturation.
The use of a simple lysis buffer during the heating process, on the other hand, will enhance the yield and quality of DNA.
Cells with a harder cell wall:
The cell wall of plant cells contains pectin and other polysaccharides. The cell is protected against mechanical harm by pectin. As a result, pectin gives the plant cell wall added strength.
Hard cell walls are also found in some fungi, algae, and bacteria, which help them survive in tough environments. We must adjust the process using a combination of mechanical, chemical, and enzymatic methods in order to extract DNA from this type of cell.
In order to isolate DNA from pectin-rich cells, mechanical lysis is necessary. Mortar, pestle, grinding, and liquid nitrogen are all employed to accomplish this.
Different types of DNA extraction methods:
DNA extraction methods are broadly categorized into two categories:
- Chemical-based DNA extraction method.
- Silica-based DNA extraction method.
The chemical DNA extraction methods are also known as solution-based methods whilst solid-phase DNA extraction is a type of physical method.
Chemical or solution-based DNA extraction method:
Various organic and inorganic solutions are used in a chemical or solution-based technique. The main steps in all procedures, namely cell lysis, precipitation, and elution, are the same.
Several popular chemicals used in the solution-based DNA extraction approach include SDS, CTAB, phenol, chloroform, isoamyl alcohol, Triton X100, guanidium thiocyanate, Tris, and EDTA.
Organic solvent-based DNA extraction and inorganic solvent-based DNA extraction are two types of solution-based (also known as chemical) DNA extraction.
Organic solvents such as phenol and chloroform are used in the organic solvent-based DNA extraction method. The current procedure is not recommended due to the dangers of phenol and chloroform. Regardless, the phenol-chloroform technique is the most effective.
The proteinase-K DNA extraction process yields a higher quantity of DNA; however, it takes a long time. Proteinase-K cannot be used for a longer period of time if it is not kept cold in a cold chain. Another important drawback with this procedure is the enzyme’s decreased stability.
The proteinase K-based approach for DNA isolation is an inorganic solution-based technology.
The salting-out DNA extraction method:
Salts such as sodium chloride, potassium acetate, and ammonium acetate are used in the salting-out DNA extraction process. However, when used in conjunction with proteinase K, the procedure produces outstanding results.
The purity of the salting-out process is one of its key drawbacks; while a sufficient yield can be reached, the quality gained may not be satisfactory.
Phenol-chloroform method of DNA extraction:
This is one of the most effective ways for extracting DNA. If we perform the PCI procedure properly, the yield and purity of DNA obtained are excellent. The PCI method of DNA extraction is also known as the phenol-chloroform-isoamyl alcohol method.
Liquefaction buffer, phenol, and chloroform are the most common chemicals used in PCI DNA extraction procedures.
Tris, EDTA, MgCl2, NaCl, SDS, and other salts are present in the lysis buffer. The components of lysis buffer aid in the lysis of both the cell membrane and the nuclear envelope in this situation. The technique’s chemical components, phenol and chloroform, denature the protein portion of cells.
Role of chemicals:
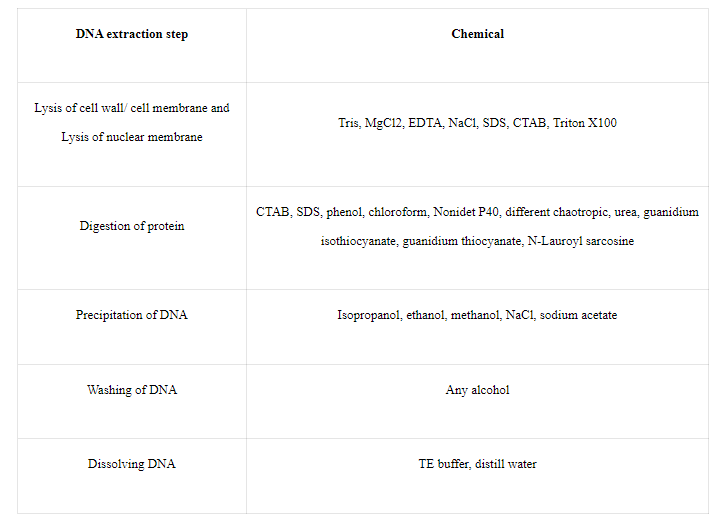
Fig: Role of several chemicals used in DNA extraction
Enzymatic method of DNA extraction:
This method is actually a combination of a salt method and an enzymatic method. Before proceeding with the enzymatic digestion, the extraction buffer is used.
The extraction buffer’s composition varies each lab, but the main ingredients are Tris, EDTA, NaCl, sodium lauryl sulfate, and SDS. No phenol, chloroform, or isoamyl alcohol is utilized in this experiment. Instead, the material is digested with the enzyme proteinase K.
Proteinase K is added to the sample and incubated for two hours, digesting all of the protein present.
The sample is immediately precipitated by cold alcohol after digestion with proteinase K. All other cell debris is removed from the sample by centrifugation. The DNA pellet is finally dissolved in TE buffer.
This DNA extraction procedure is quick and simple. We can utilize a DNA extraction buffer that is ready to use. The yield is also very high. The purity of DNA, on the other hand, is a serious concern for this approach.
Silica column-based DNA extraction method:
The silica column-based DNA extraction method is distinct from other DNA extraction techniques.
The proteinase K method requires centrifuging the sample several times and collecting the aqueous phase or pellets, depending on the extraction stage. We may need to collect an aqueous phase or pellets on occasion.
The silica-based DNA extraction method relies on the unique chemistry of silica and DNA interaction. During centrifugation, positively charged silica particles bind to negatively charged DNA and retain it in position.
The method was first described by McCormick in 1989. However, the idea was developed in 1979, when silica was used in DNA purification by Vogelstein.
The commercially accessible silica-based solid-phase DNA extraction technology is now widely employed in diagnostic laboratories. It is widely accepted because to its high-quality DNA yield and simple operating system.

Fig: Silica column-based DNA extraction method:
Application:
The commercially accessible silica-based solid-phase DNA extraction technology is now widely employed in diagnostic laboratories. It is widely accepted because to its high-quality DNA yield and simple operating system.
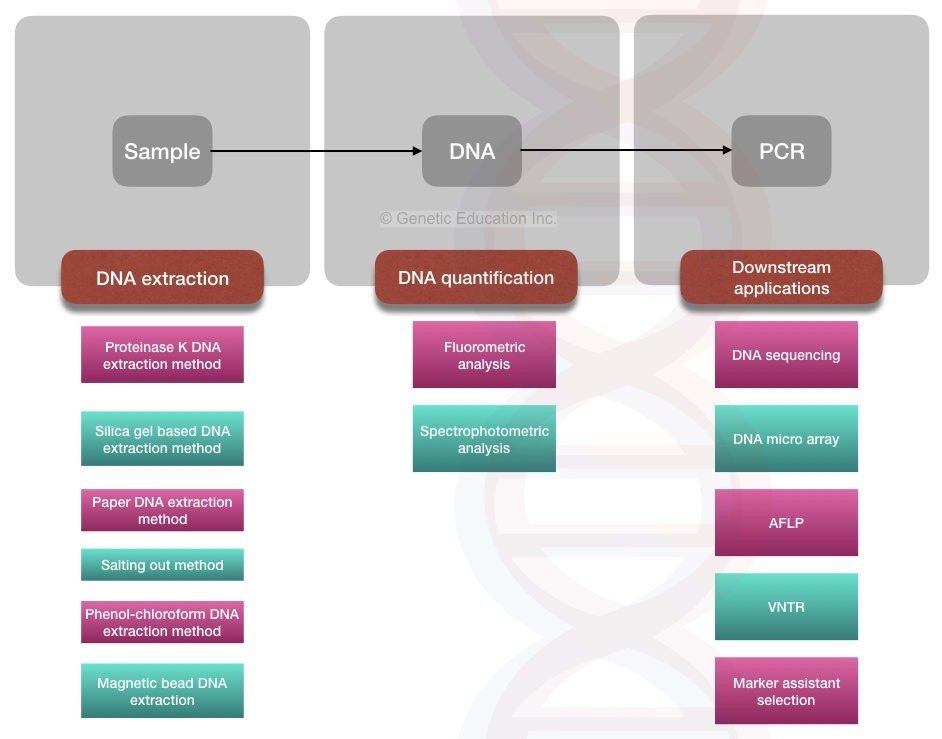
Fig: Application of DNA extraction
Method for conformation of DNA extraction/Quantification of extracted DNA:
DNA can be validated by electrophoresing on an agarose gel using ethidium bromide, or another fluorescent dye that reacts with DNA, and examining under UV light.
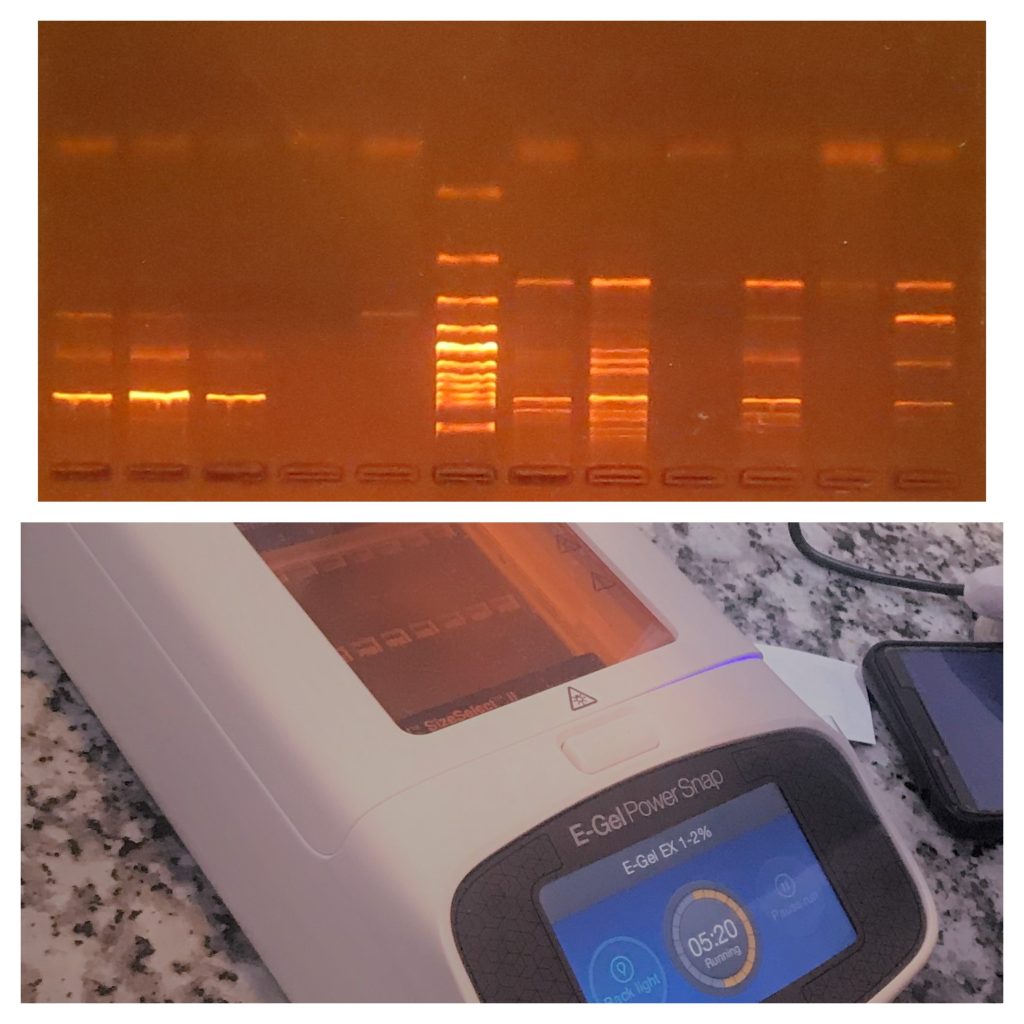
Fig: Agarose gel elctrophoresis and E-Gel electrophoresis
Absorbance Methods
- Measuring the intensity of absorbance of the DNA solution at wavelengths 260 nm and 280 nm is used as a measure of DNA purity.
- The most common purity calculation is the ratio of the absorbance at 260nm divided by the reading at 280nm. Good-quality DNA will have an A260/A280 ratio of 1.7–2.0.
- A reading of 1.6 does not render the DNA unsuitable for any application, but lower ratios indicate more contaminants are present.
Fluorescence Methods
Fluorescence measurement is another popular method for determining DNA yield and concentration due to the widespread availability of fluorometers and fluorescent DNA-binding dyes.
Fluorescence methods are more sensitive than absorbance methods, especially for low-concentration samples, and DNA-binding dyes allow for more precise DNA quantification than spectrophotometric approaches.
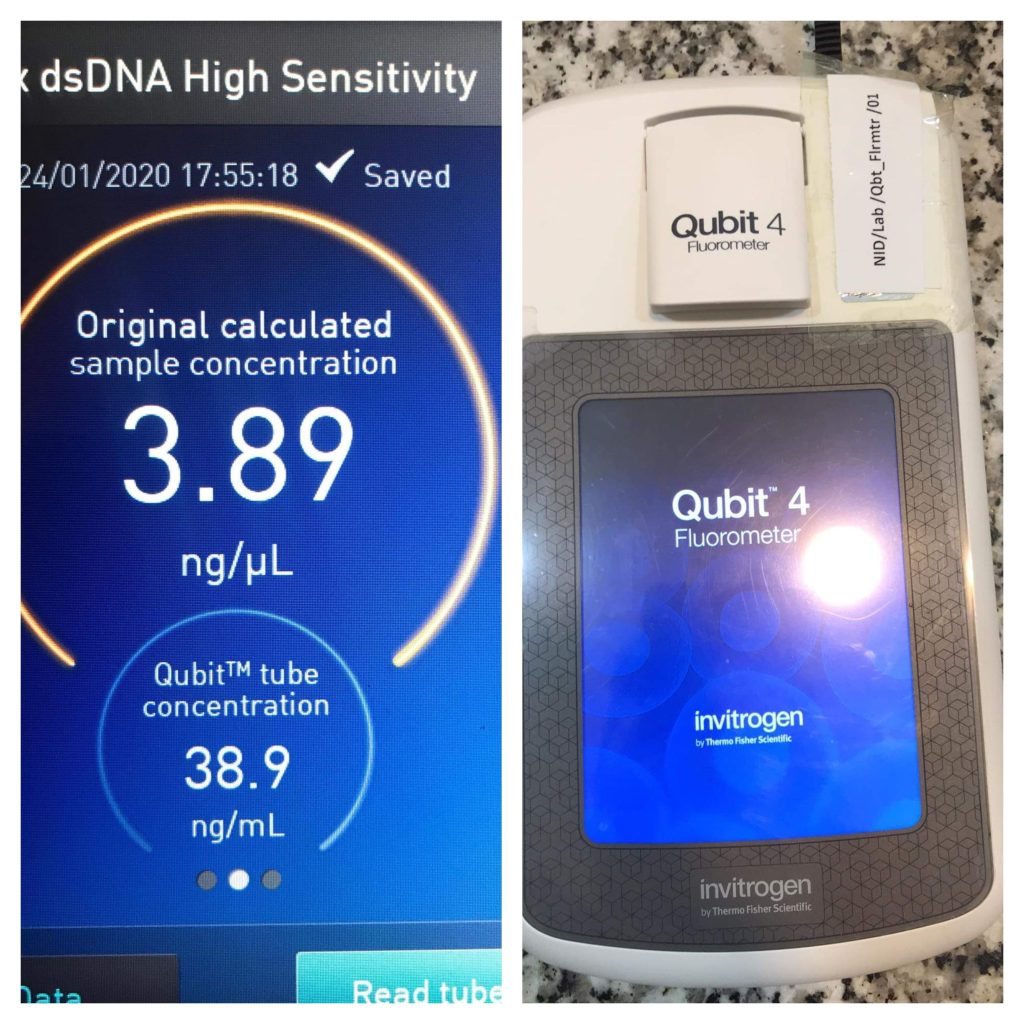
Fig: Fluorescence method for determining DNA yields
Detection of DNA:
- A diphenylamine (DPA) indicator will confirm the presence of DNA.
- This procedure involves chemical hydrolysis of DNA: when heated (e.g. ≥95 °C) in acid, the reaction requires a deoxyribose sugar and therefore is specific for DNA.
- Under these conditions, the 2-deoxyribose is converted to w-hydroxylevulinyl aldehyde, which reacts with the compound, diphenylamine, to produce a blue coloured compound.
- DNA concentration can be determined measuring the intensity of absorbance of the solution at the 600 nm with a spectrophotometer and comparing to a standard curve of known DNA concentrations.

References:
- Niemz A, Ferguson TM, Boyle DS. Point-of-care nucleic acid testing for infectious diseases. Trends Biotech. 2011; 29:240–50.
- Carpi FM, Di Pietro F, Vincenzetti S, Mignini F, Napolioni V. Human DNA extraction methods: patents and applications. Recent Pat DNA Gene Seq. 2011;5(1):1–7.
- Dahm R. Friedrich Miescher and the discovery of DNA. Dev Biol. 2005;278(2):274–288.
- Sheila Spada, … Erik Wennerberg, in Methods in Enzymology, 2020
- Dieki, R., Nsi Emvo, E. and Akue, J.P., 2022. Comparison of six methods for Loa loa genomic DNA extraction. PloS one, 17(3), p.e0265582.
- Kumar, M. and Mugunthan, M., 2018. Evaluation of three DNA extraction methods from fungal cultures. medical journal armed forces india, 74(4), pp.333-336.
- Abdel-Latif, A. and Osman, G., 2017. Comparison of three genomic DNA extraction methods to obtain high DNA quality from maize. Plant Methods, 13(1), pp.1-9.

