Introduction:
Biosafety cabinets are specialized laboratory equipment that provide a barrier between the user and the materials being handled inside the cabinet. It is an enclosed, ventilated laboratory workspace for safely working with materials contaminated with (or potentially contaminated with) pathogens. They are designed to protect the user, the materials being handled, and the environment from potential contamination or injury. Biosafety cabinets are used in a variety of settings, including research laboratories, hospitals, and other facilities where there is a risk of exposure to hazardous materials.
Features:
Airflow: Biosafety cabinets are designed to maintain a flow of air that keeps the inside of the cabinet separate from the outside environment. This airflow is typically directed from the front of the cabinet towards the back, with the air being filtered through a HEPA filter before being returned to the room.
HEPA filter: Most biosafety cabinets are equipped with a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter, which is designed to remove contaminants from the air. This helps to prevent the release of hazardous materials into the surrounding environment.
Airtight seal: Many biosafety cabinets are equipped with an airtight seal around the perimeter of the cabinet, which helps to prevent the escape of hazardous materials.
Work surface: The work surface inside a biosafety cabinet is typically made of a smooth, nonporous material that is easy to clean and disinfect.
Lighting: Biosafety cabinets are typically equipped with lighting to facilitate work inside the cabinet. Some cabinets may also have UV lighting to help kill microorganisms.
Control panel: Most biosafety cabinets have a control panel that allows the user to adjust the airflow, lighting, and other features of the cabinet.
Viewing window: Many biosafety cabinets have a viewing window that allows the user to see inside the cabinet without opening the door.
Temperature and humidity sensors: Some biosafety cabinets are equipped with temperature and humidity sensors to monitor the temperature and humidity inside the cabinet.
Pressure gauges: Pressure gauges may be used to monitor the pressure inside the cabinet to ensure that it is within the proper range.
UV lamps: Some biosafety cabinets are equipped with UV lamps to kill microorganisms and help prevent contamination.
Access ports: Some biosafety cabinets have access ports that allow the user to insert instruments or materials into the cabinet without opening the door.
Alarms: Many biosafety cabinets are equipped with alarms that alert the user if the airflow or other safety features of the cabinet are not functioning properly.
Types:
Class I biosafety cabinets
It is also known as “microbiological safety cabinets” that provide the lowest level of protection and are used for handling materials that do not pose a significant risk of infection or injury. Class I cabinets are not completely sealed and do not provide protection against hazardous chemicals or gases.
Class I BSCs are characterized by their inward airflow design, which helps to contain hazardous materials within the cabinet. Air is drawn into the cabinet through a front grille and passes over the work surface, creating a downward airflow. This helps to prevent the escape of hazardous materials from the cabinet and minimizes the risk of contamination to the operator. Class I BSCs are not suitable for handling infectious agents or toxic materials and are generally used in Biosafety Level 1 (BSL-1) laboratories.
Class II biosafety cabinets
This is also known as “biological safety cabinets” that provide a higher level of protection than Class I cabinets and are used for handling materials that may pose a moderate risk of infection or injury. Class II cabinets are sealed and provide some protection against hazardous chemicals and gases. Class II BSCs are characterized by their inward and downward airflow design, which helps to contain hazardous materials within the cabinet. Air is drawn into the cabinet through a front grille and passes over the work surface, creating a downward airflow. This helps to prevent the escape of hazardous materials from the cabinet and minimizes the risk of contamination to the operator.
Type A Class II
Type A Class II BSCs are designed to protect the operator and the environment from hazardous materials and are used to handle low-risk biological materials, such as tissue culture cells and microbial cultures. They are commonly used in Biosafety Level 1 (BSL-1) laboratories and are suitable for handling materials that pose a minimal risk of infection or contamination.
Type A Class II BSCs are characterized by their inward and downward airflow design, which helps to contain hazardous materials within the cabinet. Air is drawn into the cabinet through a front grille and passes over the work surface, creating a downward airflow. This helps to prevent the escape of hazardous materials from the cabinet and minimizes the risk of contamination to the operator.
Type A Class II BSCs are equipped with HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters, which are designed to capture particles that are 0.3 micrometers or larger in size. This ensures that the air inside the cabinet is free of contaminants and suitable for use in handling low-risk biological materials.
Type B Class II
Type B Class II biosafety cabinets (BSCs) are specialized pieces of equipment that are used in laboratories to protect the operator and the environment from exposure to potentially hazardous biological materials. They are designed to provide a contained, ventilated workspace in which to handle microorganisms, cell cultures, and other biological materials.
They are characterized by their inward and downward airflow design, which helps to contain hazardous materials within the cabinet. Air is drawn into the cabinet through a front grille and passes over the work surface, creating a downward airflow. This helps to prevent the escape of hazardous materials from the cabinet and minimizes the risk of contamination to the operator.
Type B Class II BSCs are equipped with HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters, which are designed to capture particles that are 0.3 micrometers or larger in size. This ensures that the air inside the cabinet is free of contaminants and suitable for use in handling moderate- to high-risk biological materials.
There are two types of Type B Class II BSCs: Type B1 and Type B2.
Type B1 Class II BSCs
They are designed to protect the operator and the environment from hazardous materials and are used to handle moderate-risk biological materials, such as viral cultures and hazardous chemicals. They are commonly used in Biosafety Level 2 (BSL-2) laboratories and are suitable for handling materials that pose a moderate risk of infection or contamination.
Type B2 Class II BSCs
They are designed to protect the operator and the environment from hazardous materials and are used to handle high-risk biological materials, such as pathogens and toxins. They are commonly used in Biosafety Level 3 (BSL-3) laboratories and are suitable for handling materials that pose a high risk of infection or contamination.
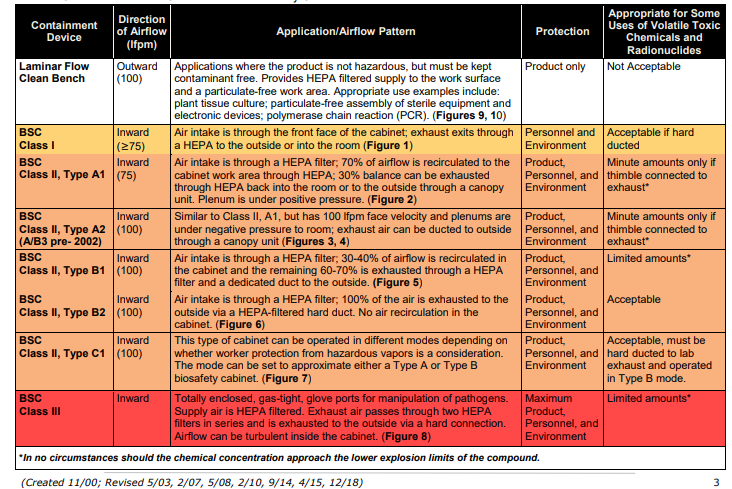
Fig: Types of Biosafety cabinets
Class III biosafety cabinets
This is also known as “high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter cabinets” that provide the highest level of protection and are used for handling materials that pose a high risk of infection or injury, such as hazardous chemicals, radioactive materials, and infectious agents. Class III biosafety cabinets (BSCs) are specialized pieces of equipment that are used in laboratories to protect the operator and the environment from exposure to potentially hazardous biological materials. They are designed to provide a contained, ventilated workspace in which to handle microorganisms, cell cultures, and other biological materials.
Class III BSCs are used in Biosafety Level 4 (BSL-4) laboratories and are suitable for handling materials that pose a high risk of infection or contamination, such as highly infectious agents and toxins. They are characterized by their positive pressure design, which helps to prevent the escape of hazardous materials from the cabinet. Air is supplied to the cabinet at a higher pressure than the surrounding room, creating a positive pressure inside the cabinet. This helps to prevent the entry of contaminants into the cabinet and minimizes the risk of contamination to the operator.
Class III BSCs are equipped with HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters, which are designed to capture particles that are 0.3 micrometers or larger in size. This ensures that the air inside the cabinet is free of contaminants and suitable for use in handling high-risk biological materials. Class III BSCs also have a specialized ventilation system that is designed to exhaust air from the cabinet to the outside of the building. This helps to prevent the release of hazardous materials into the environment.
Standard Operating Procedures:
SOPs may include instructions on how to properly set up and use the BSC, how to properly handle hazardous materials inside the BSC, and how to properly maintain and decontaminate the BSC. It is important to follow SOPs for the use of BSCs carefully to ensure the safety of the user and the surrounding environment. SOPs should be reviewed regularly to ensure that they are up-to-date and relevant to the tasks being performed.
- Only trained personnel should use the BSC.
- The BSC should be placed in a well-ventilated area and should be inspected regularly to ensure that it is functioning properly.
- The BSC should be decontaminated regularly using approved disinfectants (i.e., 10% bleach followed by 70% ethanol).
- All hazardous materials should be properly labeled and stored.
- The BSC should be used for activities that generate aerosols or splashes only.
- The BSC should not be used to store food or drink and should be turned off when not in use.
- Wearing the proper personal protection equipment (PPE) is required. Lab coat buttons are required. Instead of being worn inside the coat, gloves should be pulled over the lab coat’s wrists. Use of additional PPE is highly advised.
- Before removing anything from the BSC, decontaminate all surfaces and objects. Gather all waste materials in an autoclave bag, and autoclave according to the proper protocols.
Applications:
Biosafety cabinets (BSCs) are specialized pieces of equipment that are used in laboratories to protect the operator and the environment from exposure to potentially hazardous biological materials. BSCs are designed to provide a contained, ventilated workspace in which to handle microorganisms, cell cultures, and other biological materials. They are commonly used in research, clinical, and industrial settings for a variety of applications, including:
- Handling and processing of infectious agents and toxins.
- Preparation and handling of cell cultures and other biological materials.
- Microbiological and molecular biology procedures.
- Quality control testing of pharmaceutical and other products.
- Training and educational purposes.
References:
- Ficociello, B., Giordano, D., Incoronato, F., Farinella, A. and Pietrangeli, B., 2022. WHO Laboratory Biosafety Manual: A New Approach to Security. Annals of Work Exposures and Health.
- World Health Organisation Staff and World Health Organization, 2004. Laboratory biosafety manual. World Health Organization.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, N. I. (2007). Biosafety in Microbiological and Biomedical Laboratories (5th Edition ed.). Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office
