Diagnosis of Vibrio cholerae
Culture methods:
- Bacterial culture is the gold standard for confirmation of Vibrio cholera in a sample. Sample of choice is the rice water stool.
- Prior enrichment step (4–6 hours at 37℃), in alkaline peptone water (APW, pH 8.0) is preferred especially in non-acute or chronic cases.
- Selective plating is performed by the inoculation on selective Thiosulfate Citrate Bile Salt Sucrose (TCBS) agar or Taurocholate-Tellurite-Gelatin Agar (Monsur medium) or on Chromogenic medium such as CHROMagar. On TCBS agar after overnight incubation, typical V. cholerae colonies appear as 2-4 mm, shiny yellow color colonies due to sucrose fermentation.
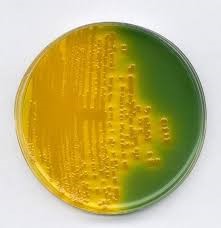
Fig: Vibrio cholerae on TCBS
- On Monsur’s media after overnight incubation, Vibrio cholerae are seen as 1-2mm, “gunmetal” grey colonies
- On CHROMagar, Vibrio cholerae appear green blue to torquise blue.
- On Gelatin Agar (GA), Gelatinase activity characteristic of Vibrio is indicated by production of opaque zone around colonies which resemble halo. Halo effect can be intensified by brief refrigeration of plate. Salt free GA can be used to rule out halophilic Vibrio resembling Vibrio cholerae
- Meat Extract Agar (MEA) similar to GA but doesn’t produce differential characteristics. Under obliquely transmitted light, Vibrio cholerae colonies appear granular with greenish sheen on both media.
Biochemical identification:
| Test | V. cholerae |
| KIA (Kligler’s Iron Agar) | K/A |
| TSI (Triple Sugar Iron) | A/A |
| String | + |
| Oxidase | + |
| Gas from glucose | – |
| Sucrose | + |
| Lysine | + |
| Arginine | – |
| Ornithine | + |
| VP (Voges-Proskauer ) | V |
| Growth in 0% NaCl | + |
| Growth in 1% NaCl | + |
String test:
Using a glass, the suspected Vibrio cholerae 18-24-hour growth is mixed in a drop of 0.5% aqueous solution of sodium deoxycholate and mucoid string forming bacterial cell is observed using an inoculating loop to pick the suspension slowly away from the slide.
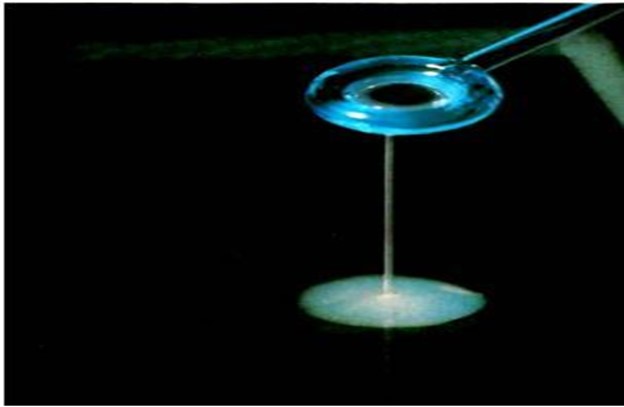
Fig: String test
Wet Mount Examination:
Dark-field and phase-contrast microscopy are employed. Freshly collected rice-water stool as a sample of choice. Saline suspensions are microscopically examined for the presence of organisms with darting motility. Motility detection improved by using V. cholera O1 antisera
Serological diagnosis:
Presumptive identification can be performed by Sero grouping using 0-group specific polyvalent antisera. Serotyping using type-specific monovalent antisera to differentiate Ogawa, Inaba and Hikojima serotypes. uSerotyping of V cholera serogroupO1:
| Serotype | Major O factor present | Ogawa antisera agglutination | Inaba antisera agglutination |
| Ogawa | A, B | + | – |
| Inaba | A, C | – | + |
| Hikojima | A, B, C | + | + |
Rapid tests:
| Test | Specimen | Sensitivity | Specificity |
| Sensitive Membrane Antigen Rapid Test (SMART) | Stool | 83% | 88% |
| SD Bioline | Stool and APW | 91-95% | 95-100% |
| Cholkit | Stool | 98% | 96% |
| Crystal VC | Stool and (APW) | (62-81%) | 91-100% |
Immunoassay:
Coagglutination
Coagglutination detects micrograms of soluble Vibrio cholera 01 and 0139 antigen in stool or APW enriched stool sample by the virtue of outer coat of protein A of Staphylococcus aureus Cowan I strain when sensitized with high titer of Vibrio cholera 01 or 0139 antisera.
Latex agglutination
Specific anti-Cholera Toxin bound antisera bound to latex particles can be used.
Detection of Cholera Toxin encoding gene:
PCR detects V. cholerae strains not expressing Cholera Toxin at detectable levels but possess ctx genes. Several PCR variation are generally employed to detect CT subunit A. The amplified DNA from ctxA is detected as a 564-bp band in an agarose gel. The PCR amplicon can be further characterized by hybridization probe hybridization to ensure the ctxA gene in gel.
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing ATCC 25922 is used for accurate V. cholerae susceptibility with each test. There has been an extension of V. cholerae from penicillanases or β-lactamases of various class to carbapenemases. Multi Drug Resistance (MDR) V. cholerae with epidemic outbreaks (both classical and El Tor biotypes) have been reported worldwide. For MDR V. cholerae, ciprofloxacin is used as substitute drug for treatment. Alternative to ciprofloxacin resistance are the third generation cephalosporins. A multiplex PCR can be used to detect carbapenemase genes, i.e., blaKPC, blaIMP, blaVIM, and blaNDM and ESBL genes, i.e., blaCTX, blaSHV, and
