Introdcution:
The liverwort Marchantia polymorpha L., is one of the model organisms representing a basal group of land plants. It is one of the common weeds that grows in nursery crop production and distributed widely around the world from tropical to arctic climates.
Plant chloroplast genomes are far more structurally conserved than plant mitochondrial genomes. These genomes are circular and the size of higher plant chloroplast DNAs either 150kb (for example, spinach) or 120 (for example pea). The difference in size can be accounted for by deletion from the larger genome to generate the smaller.
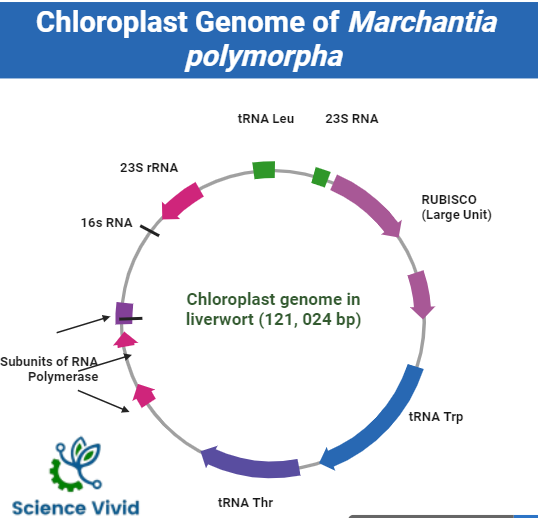
Fig: Chloroplast Genome: The liverwort Marchantia polymorpha L.
Genome makeup:
Many chloroplast DNA genes encode proteins which are involved in photosynthesis. In total, the genome appears to encode all rRNA and tRNA genes, as well as 45 protein products. There are occasional variations between species, although these are mostly between higher plants and algae, which also possess chloroplast DNA.
The genome of the chloroplasts found in Marchantia polymorphia, one of the Bryophytes contains 121,024 base pairs in a closed circle that make up some 128 genes.
The liverwort chloroplast DNA has 121,024 base pairs (bp) and is made up of a set of large inverted repeats (IRA and IRB, each with 10,058 bp) separated by a large single-copy region (LSC, 81,095 bp) and a small single-copy region (SSC, 19,813 bp).
- Duplicate genes encoding each of the four subunits (23S, 16S, 4.5S and 5S) of the rRNA used by the chloroplast.
- All of the transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules required for translation within the chloroplast are encoded by 37 genes.
- Four genes encode some of the RNA polymerase subunits utilized for transcription in the chloroplast.
- A gene encoding the large subunit of the enzymes RUBISCO (Ribulose biphosphate carboxylase oxygenase).
- 9 genes for components of photosystem I and II
- 6 genes encoding parts of the chloroplast ATP synthase
- Genes for 19 of the around 60 proteins used to construct ribosome
All of these gene products are utilized within the chloroplast, yet all chloroplast structures rely on proteins expressed by nuclear genes.
